- Home Page
- Managed ICT & IT Services
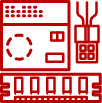
- Security Services
- Disaster Recovery as a Service
Disaster Recovery
as-a-Service
To be the best, you have to be able to handle the worst
Enquire Now



What is Disaster Recovery as a Service - DRaaS ?
DRaaS is a standalone offering that 'provides for the recovery of enterprise applications at another location in the event of a disaster.' -Gartner 2022
In an age of SaaS, Disaster Recovery-as-a-Service [DRaaS] is a practical option for businesses who don’t have the resources – staffing or technology – to have disaster recovery, inhouse.
DRaaS has many benefits that include reduced disaster recovery cost, increased simplicity, reduced IT resources required, and maximum efficiency provided.
Why to consider adopting Disaster-Recovery-as-a-Service
It’s going to happen, sometime…
Are your business-critical applications vulnerable to an extended outage or disaster at your primary infrastructure location?
There is one thing that is as certain as death and taxes – at some point in time your business systems will go down.
When it happens… knowing there is a plan in place, that it has been well-tested, and that specialists will swing into action to implement it… that’s priceless.

MobileCorp Disaster Recovery as a Service (DRaaS)
MobileCorp partners with market-leading vendors to provide a comprehensive ‘Disaster Recovery as a Service’ module.
Disaster Recovery involves a set of policies, tools and procedures that ensure the recovery or continuation of all vital technology infrastructure and systems following a natural or human-induced disaster.
However, before recommending any specific solution, MobileCorp will understand and evaluate your IT environment, business drivers, current capabilities, limitations and budget.
MobileCorp Disaster Recovery Planning
A MobileCorp DR plan will include seven key elements:
- Disaster Recovery Goals
- Redundancy
- Business Continuity
- Documentation
- Prioritised Business Functions
- Internal Communications
- Testing and Optimisation
1. Disaster Recovery Goals
When drafting a disaster recovery plan, it’s important to first assess the goals the plan will aim to accomplish. These will include:
- Risk Reduction
A primary goal of a good disaster recovery plan is to reduce an enterprise’s overall risk. Companies should conduct a current risk assessment before forming the plan to understand where vulnerabilities exist that need to be addressed. You can use a number scale to measure each risk level.
- Resumption of Operations in an Emergency
When a disaster occurs, a DR plan should be ready to go pushing out information and solutions to internal and external customers, resuming operations as quickly as possible.
- Address Owner/Investor Concerns
For enterprise businesses, a disaster recovery plan should communicate to whoever is at the top of the organisation – be it owners, investors, a board of directors or shareholders.
- Regular Maintenance
A disaster plan should be updated regularly. A DRaaS will run routine risk assessments on a schedule and ensure the disaster recovery plan addresses all risks at any given time. As the organisation changes, new technologies must be added into the plan.
- Narrow Disaster Response Times
A key piece of any disaster recovery plan is ensuring that the DR team and other disaster recovery stakeholders can mobilise quickly and in a coordinated way. To narrow disaster response time, enterprise businesses should routinely test their plan at least once per year.
- Industry Compliance
Creating an effective DRP will reduce the risk of incurring penalties for failure to meet regulatory compliance obligations.
2. Redundancy
Server virtualisation has removed the need for duplicate server hardware, making redundancy more cost effective. It is now easier to shift key servers for additional capacity and maintain operations if primary systems fail.
3. Business continuity
Many hosting providers offer highly scalable platforms on which companies of all sizes can build DR environments. If a disaster occurs at the main business premises, key systems can be redirected to the hosted environment and the business can resume operations as quickly as possible.
4. Documentation
It’s important to methodically document the IT infrastructure environment including related support and technical contacts, and server and application configurations. Developing recovery time objectives (RTO) and recovery point objectives (RPOs) is also key.
5. Prioritised Business Functions
It will be critical to detail each IT function and the likely impact should it be interrupted. Mapping out internal dependencies and potential alternative suppliers or staff that can be brought on if necessary, can also help businesses function in the face of a disaster.
6. Internal Communications 
What are the lines of communication to be followed in the face of an emergency? These need to be clearly defined prior to an event to ensure chain of command and clarity of roles is acknowledged by all stakeholders.
7. Testing and Optimisation
It is vital to test a business recovery plan in real-world scenarios and use the insights that emerge to continually optimise the DR plan. At a minimum, the DR plan should be tested annually.
News and Insights from MobileCorp
From the TechTalk blog
Speak to our MobileCorp Representative
To get started with a technology solution, call us on 1800 243 252
Enquire Now